In our technology-driven world, optical materials play a pivotal role across various sectors, from telecommunications to medical diagnostics. The ability to manipulate light—its absorption, reflection, and transmission—affects advancements in multiple domains such as OLED displays, industrial sensors, and even cancer therapies. Unfortunately, controlling the way these materials interact with light can be both financially burdensome and technically challenging. High production costs, reliance on rare materials, and demanding manufacturing processes have made optical materials somewhat inaccessible for widespread use. Researchers are continuously on the lookout for innovative methods to produce these materials more efficiently and affordably.
A groundbreaking study by a team from Shinshu University in Japan has identified pencil lead as a potential solution for developing optical materials more sustainably and cost-effectively. Unlike traditional optical materials that often require complex and costly manufacturing methods, pencil lead is ubiquitous and readily available. The research, spearheaded by Professor Hiroshi Moriwaki and Associate Professor Shouhei Koyama, has unveiled a unique technique to harness the properties of pencil lead by employing plasma technology.
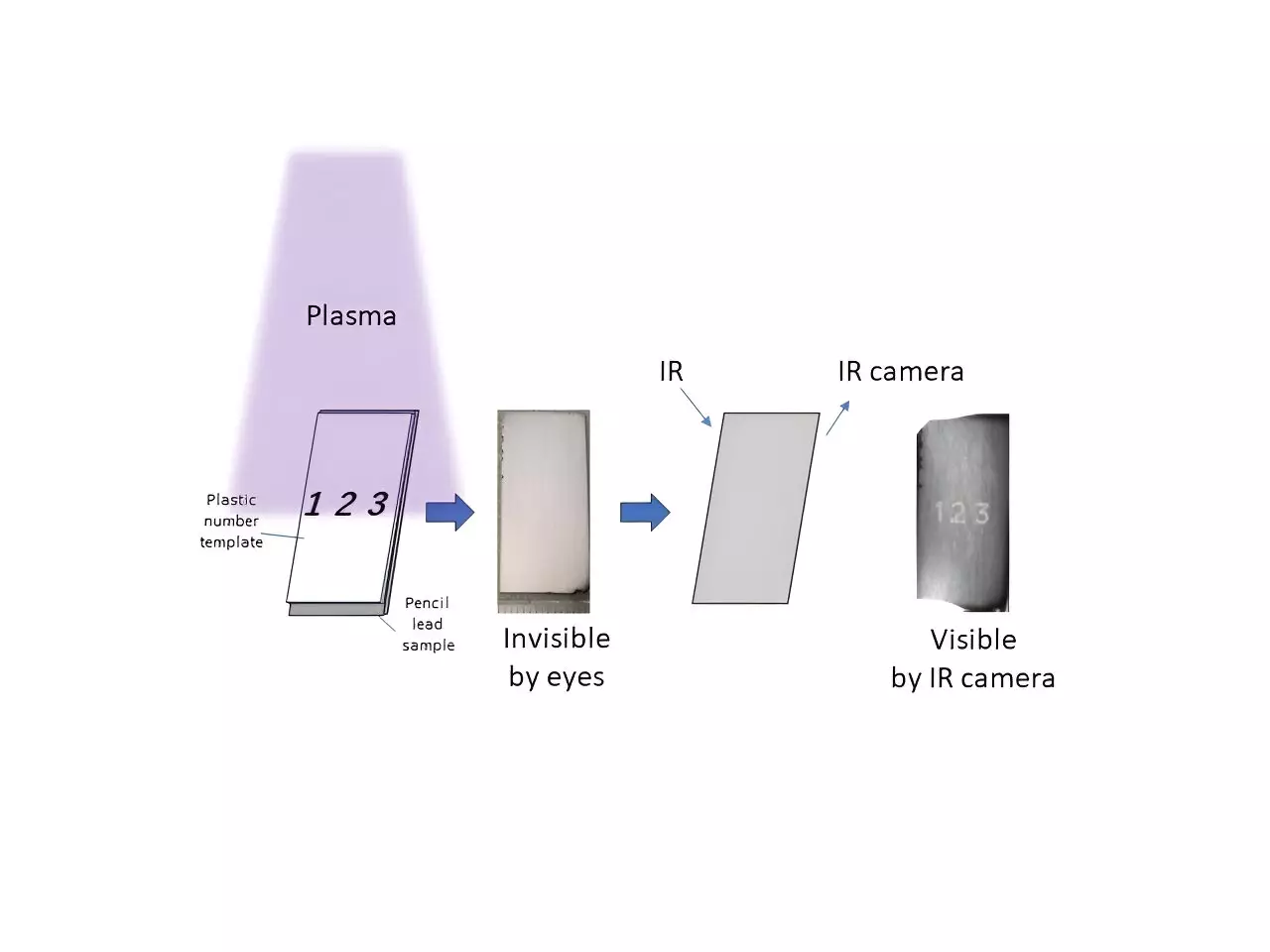
In a recent paper published in the journal Optical Materials, the researchers explain their discovery in managing the reflectance spectra of pencil lead. Initially dismissed as an ordinary writing implement, pencil lead’s primary components—clay and graphite—have now been reprised for their optical capabilities. This transformation relies on a method known as plasma etching, which can affect the layered structure of pencil lead to create new optical phenomena.
The excitement surrounding this study stems from the researchers’ ability to manipulate light through plasma. Plasma, an ionized state of matter, was applied to pencil lead samples, allowing the interaction with light to be finely tuned. The process of etching away graphite exposes the underlying clay, enabling interference patterns to form—an effect known as thin-layer interference.
The innovation does not merely stop at the creation of vibrant structural colors. The team’s investigations revealed that extended plasma irradiation durations led to the generation of materials with distinct optical properties in the near-infrared and mid-infrared ranges, which fall outside the realm of visible light. By conducting a series of experiments involving different irradiation timeframes, the researchers found remarkable changes in the reflectance spectra of the altered pencil lead.
Perhaps one of the most astonishing applications showcased in this research is the ability to create invisible markings on the surface of pencil lead that can only be detected using an infrared camera. By etching choices of letters and numbers, they have opened a door to potential uses in security features or nuanced printing techniques. This innovative approach not only highlights the versatility of pencil lead as an optical material but also presents exciting possibilities for a new generation of printing technology.
As Professor Moriwaki aptly puts it, the pursuit of this research aims to breathe new life into an aged material. By employing widely available resources like pencil lead and creating eco-friendly optical materials, there is significant promise for mass adoption and sustainability.
The implications of this discovery are vast. The research team envisions a future where sustainable and affordable optical materials can democratize access to technologies that rely on light manipulation. If successful, their methodology could pave the way for widespread adoption, potentially even incorporating these technologies into existing printing solutions.
In addition to addressing cost and accessibility, the environmental implications are noteworthy. Current optical materials often necessitate materials that are not only expensive but also limited in availability. By focusing on pencil lead, a resource that is abundant and easy to source, the researchers have tapped into a groundbreaking avenue for reducing environmental impact. As industries look toward more sustainable solutions, this research offers hope for revolutionizing the field of optical materials.
The work undertaken by the Shinshu University team is a strong reminder of the potential that lies in reexamining everyday substances. By innovatively applying plasma technology to pencil lead, they have set the stage for a transformative approach to optical materials that is more affordable, sustainable, and versatile. The future of optical technology may well rest in the creativity and resourcefulness reflected in this remarkable study.